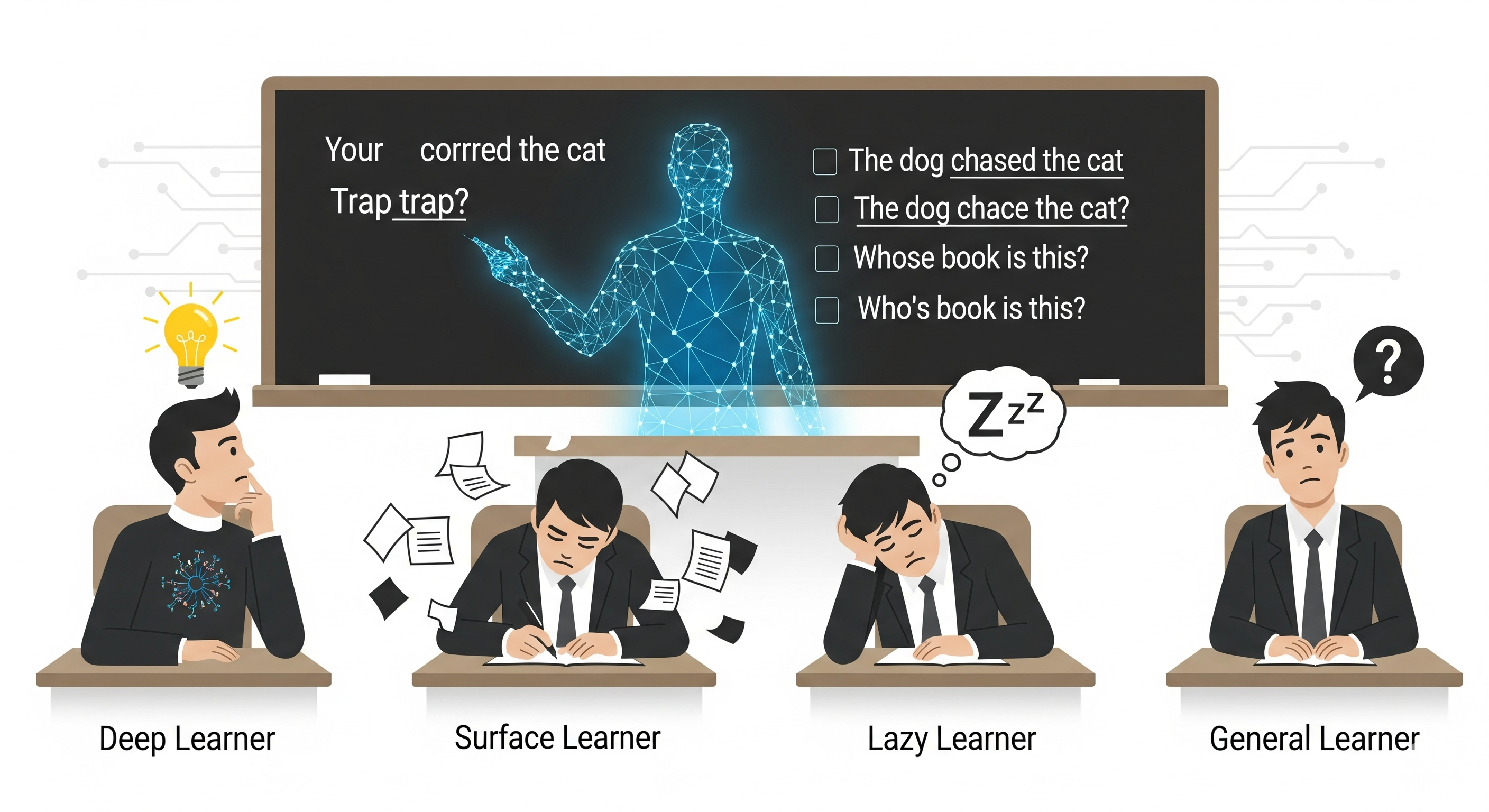
From Zero to Reasoning Hero: How R-Zero Teaches Itself Without Human Data
In AI development, removing humans from the training loop has long been a holy grail — not because people aren’t valuable, but because human labeling is expensive, slow, and fundamentally limited. R-Zero, a new framework from Tencent AI Seattle Lab, takes a decisive step in that direction: no seed dataset, no human annotations, and no external verifier. Just two AI roles — Challenger and Solver — locked in an evolutionary arms race. ...