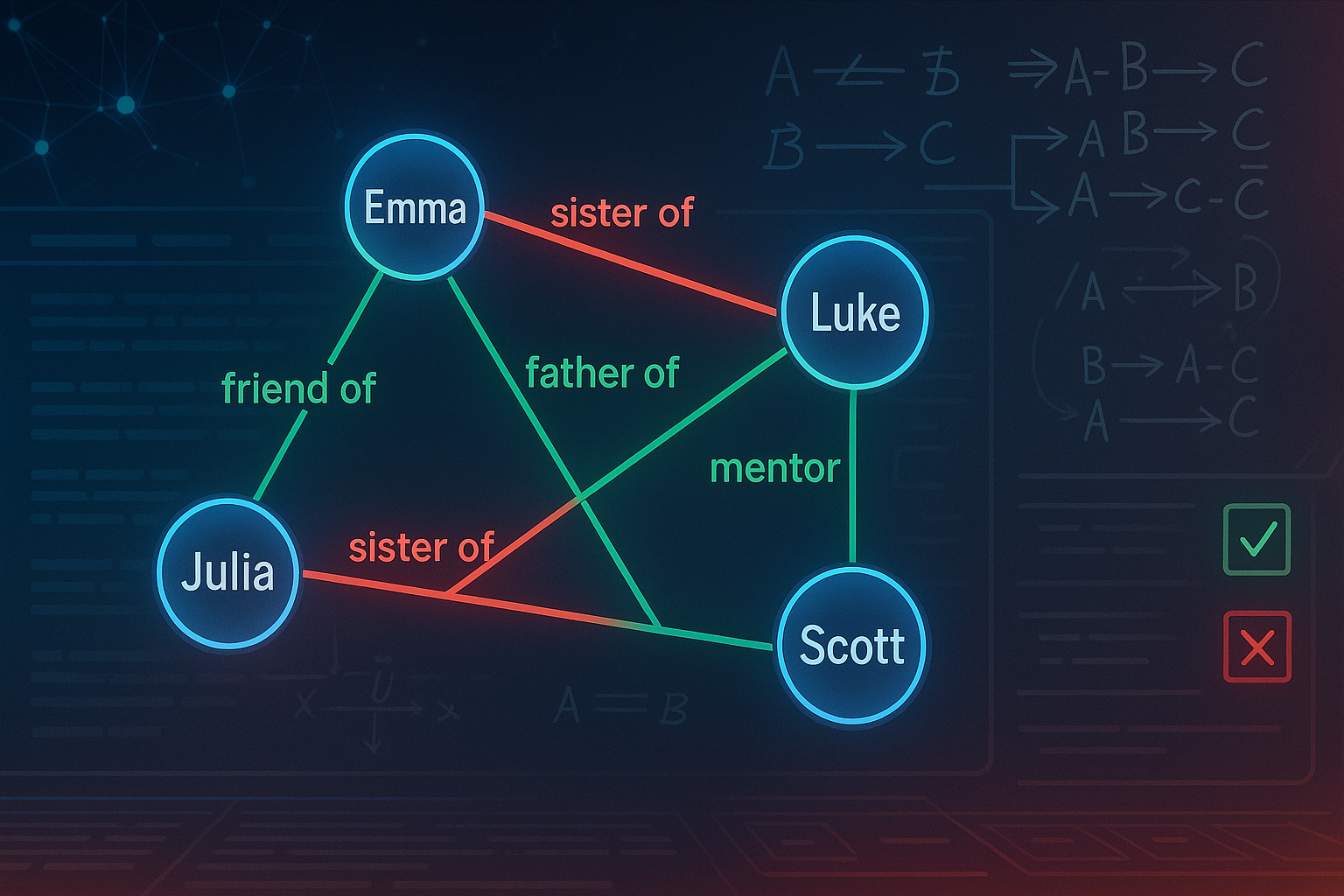
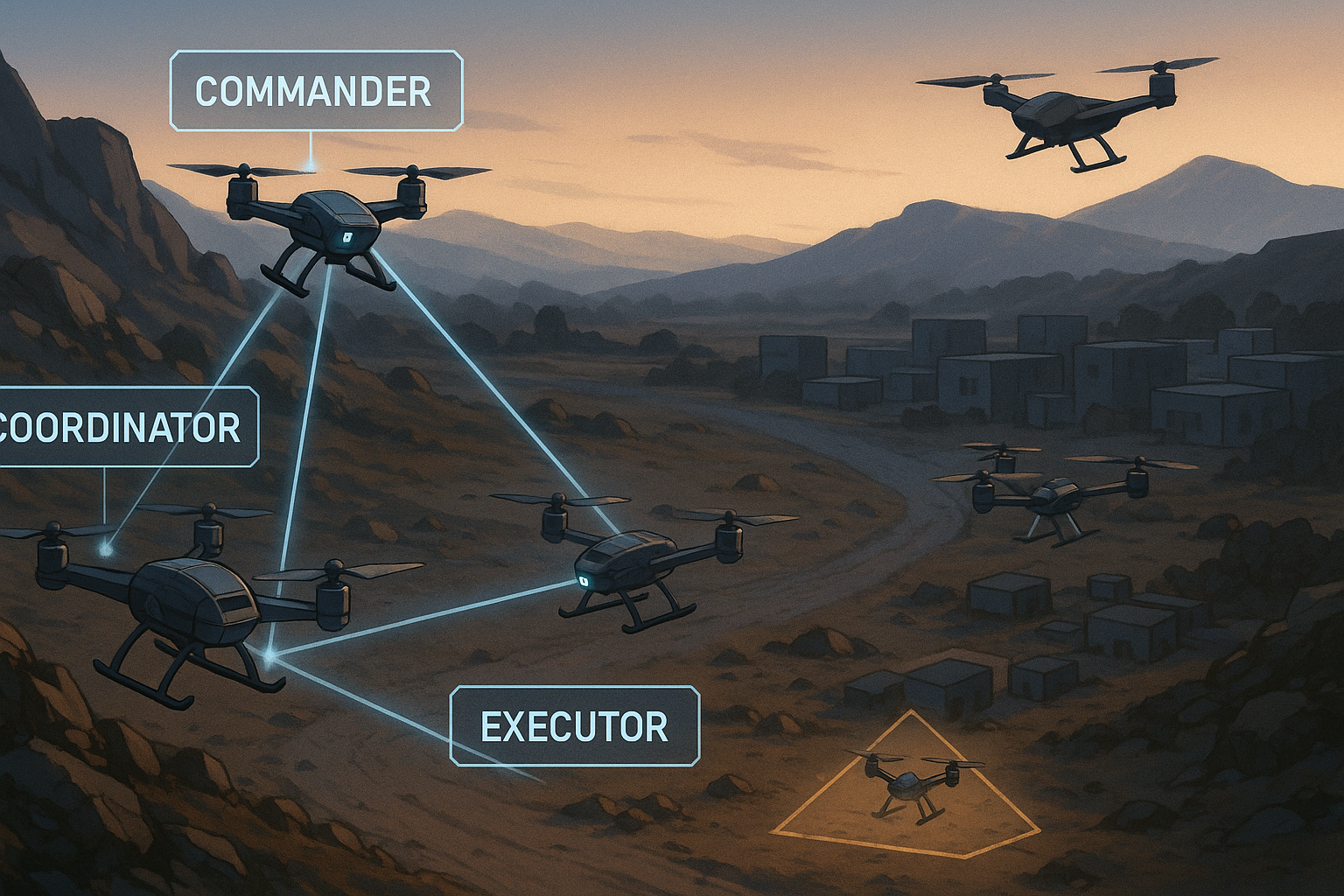
The Rise of the Self-Evolving Scientist: STELLA and the Future of Biomedical AI
When was the last time a machine truly surprised you—not with a quirky ChatGPT poem or a clever image generation, but with scientific reasoning that evolved on its own? Meet STELLA, an AI agent for biomedical research that doesn’t just solve problems—it gets better at solving them while solving them. The Static Curse of Smart Agents Modern AI agents have shown promise in navigating the labyrinth of biomedical research, where each inquiry might require cross-referencing papers, running custom bioinformatics analyses, or interrogating molecular databases. But the vast majority of these agents suffer from a fatal limitation: they rely on static, pre-installed toolkits and hard-coded logic trees. Like a PhD student who memorized a textbook but never updated it, they can’t adapt to new tasks or new knowledge without human intervention. ...