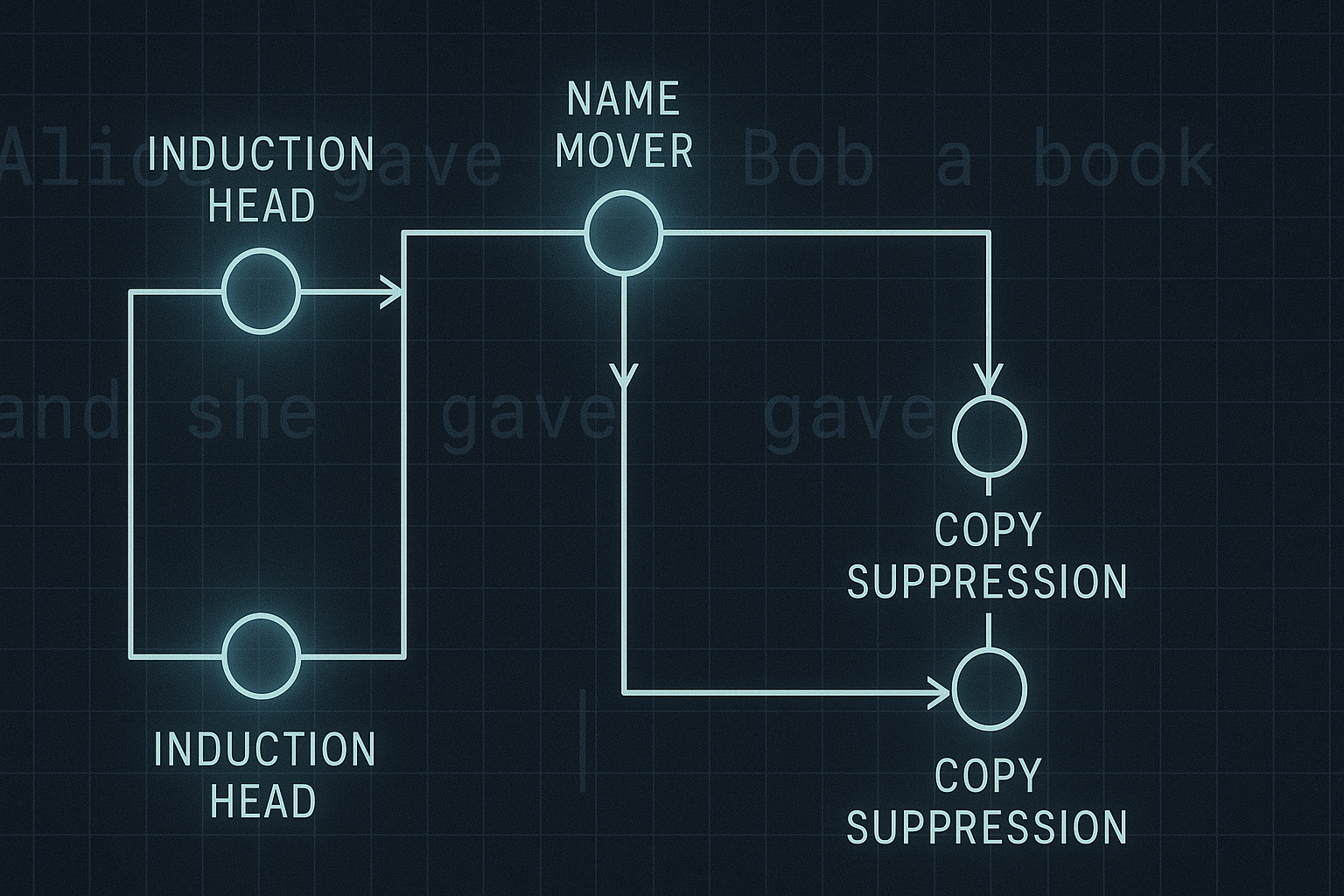
Introduction In recent years, Transformer models have redefined the field of artificial intelligence—especially in natural language processing (NLP). But their influence now stretches far beyond just language. From asset forecasting to automating enterprise tasks, Transformer architectures are laying the groundwork for a new generation of intelligent, cost-effective, and reliable SaaS platforms—especially for small businesses.
This article explores:
The core differences between Transformer models and traditional machine learning approaches. How Transformers are being used outside of NLP, such as in finance and quantitative trading. Most importantly, how Transformer-based models can power next-gen SaaS tailored for small firms. Transformer vs. Traditional Models: A Paradigm Shift Traditional machine learning models—such as logistic regression, decision trees, and even RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks)—typically process data in a fixed, sequential manner. These models struggle with long-term dependencies, require hand-engineered features, and don’t generalize well across different tasks without significant tuning.
...