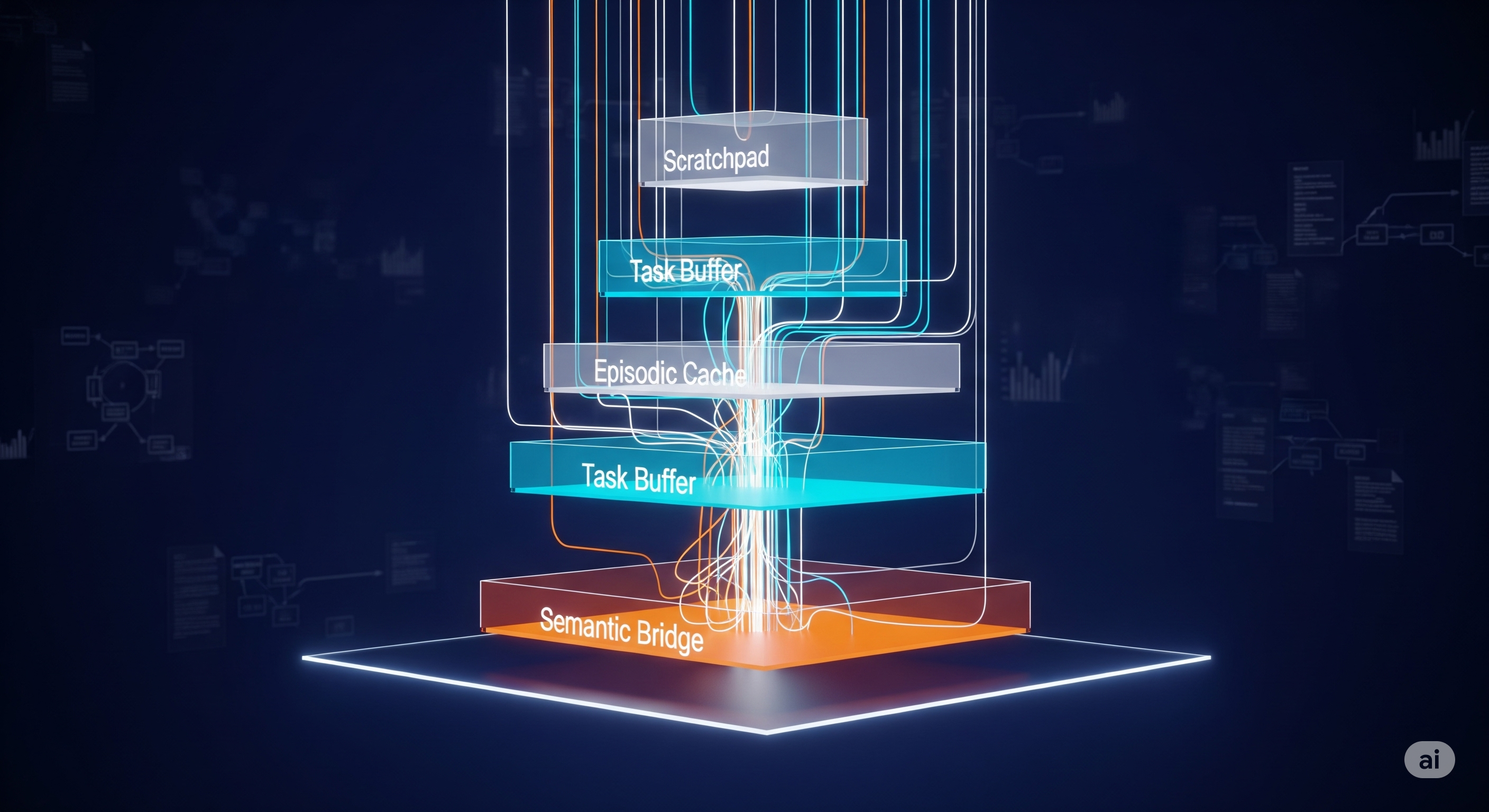
Memory With Intent: Why LLMs Need a Cognitive Workspace, Not Just a Bigger Window
TL;DR Today’s long-context and RAG systems scale storage, not thinking. Cognitive Workspace (CW) reframes memory as an active, metacognitive process: curate, plan, reuse, and consolidate. In tests, CW reports ~55–60% memory reuse and 17–18% net efficiency gains despite a 3.3× operation overhead—precisely because it thinks about what to remember and why. The Setup: Context ≠ Cognition Over the past 18 months we’ve cheered >1M-token windows and slicker attention kernels. But piling tokens into a context is like dumping files on a desk; it’s storage without stewardship. In knowledge work, what moves the needle is not how much you can “see” but how well you organize, recall, and reuse—with intent. ...