Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from a promising concept to a critical driver of business scalability, particularly within complex industries like insurance. Large Language Models (LLMs) now automate knowledge-intensive processes, transforming workflows previously constrained by manual capacity. However, effective AI-driven automation involves more than technical deployment—it demands nuanced strategic adjustments, comprehensive understanding of workflow dynamics, and meticulous validation.
In this detailed case study, Cognaptus Insights examines how If P&C Insurance, a leading insurer operating across the Nordic and Baltic regions, leveraged AI-driven Business Process Automation. The study employs Object-Centric Process Mining (OCPM) as an analytical lens, providing a robust framework for evaluating impacts, uncovering subtle workflow interactions, and formulating evidence-based best practices.1
Background: Understanding the Bottleneck
If P&C Insurance manages over 1.4 million claims annually, presenting significant operational scalability challenges. A particularly resource-intensive task within this framework was identifying specific claim parts requiring specialized processing. Historically, claim handlers manually analyzed complex, unstructured descriptions, successfully identifying relevant parts in only 1.8% of claims. This manual limitation significantly impeded overall scalability and highlighted clear inefficiencies ripe for automation.
AI Intervention: Comprehensive Process Reengineering
To address this limitation, If Insurance adopted a structured Business Process Reengineering (BPR) methodology encompassing six distinct phases:
- Understanding Phase: Conducted detailed stakeholder interviews, analyzed existing process documentation, and identified manual bottlenecks and scalability constraints.
- Initiation Phase: Defined the AI project’s scope, vision, and objectives, laying out data requirements and necessary model functionalities.
- Model Development: Leveraged GPT-4o, fine-tuned specifically for insurance claim contexts. The AI model utilized advanced prompt engineering and structured outputs, emphasizing recall to minimize missed cases.
- Transformation Phase: Implemented pilot projects to evaluate preliminary AI integrations, anticipating organizational changes and resource requirements.
- Implementation Phase: Fully integrated AI into existing IT infrastructure, adhering strictly to data privacy protocols and leveraging Azure OpenAI services.
- Evaluation Phase: Employed Object-Centric Process Mining (OCPM) to rigorously assess AI impact on the claims identification process.
The GPT-4o model, crucially optimized for high recall, successfully identified relevant claim parts in 27.6% of cases, marking a substantial 14-fold improvement over manual processes.
Evaluating Impact: The Nuances of OCPM
Traditional process mining, limited in scope, often overlooks intricate interactions within hybrid (manual and automated) workflows. Object-Centric Process Mining (OCPM), by contrast, offers a multi-dimensional analysis, capturing interactions between various workflow components and stakeholders simultaneously.
OCPM analysis at If Insurance revealed nuanced insights:
- Immediate efficiencies: AI significantly accelerated claim identification processes.
- Emerging constraints: Increased AI efficiency inadvertently shifted bottlenecks downstream, overwhelming investigators responsible for evaluating flagged claim parts.
This finding underscores a critical insight: isolated automation often redistributes workload challenges rather than resolving them outright. It emphasizes the importance of anticipating secondary effects of process changes through comprehensive data-driven evaluation.
Fig. 1: Business Process Reengineering Framework
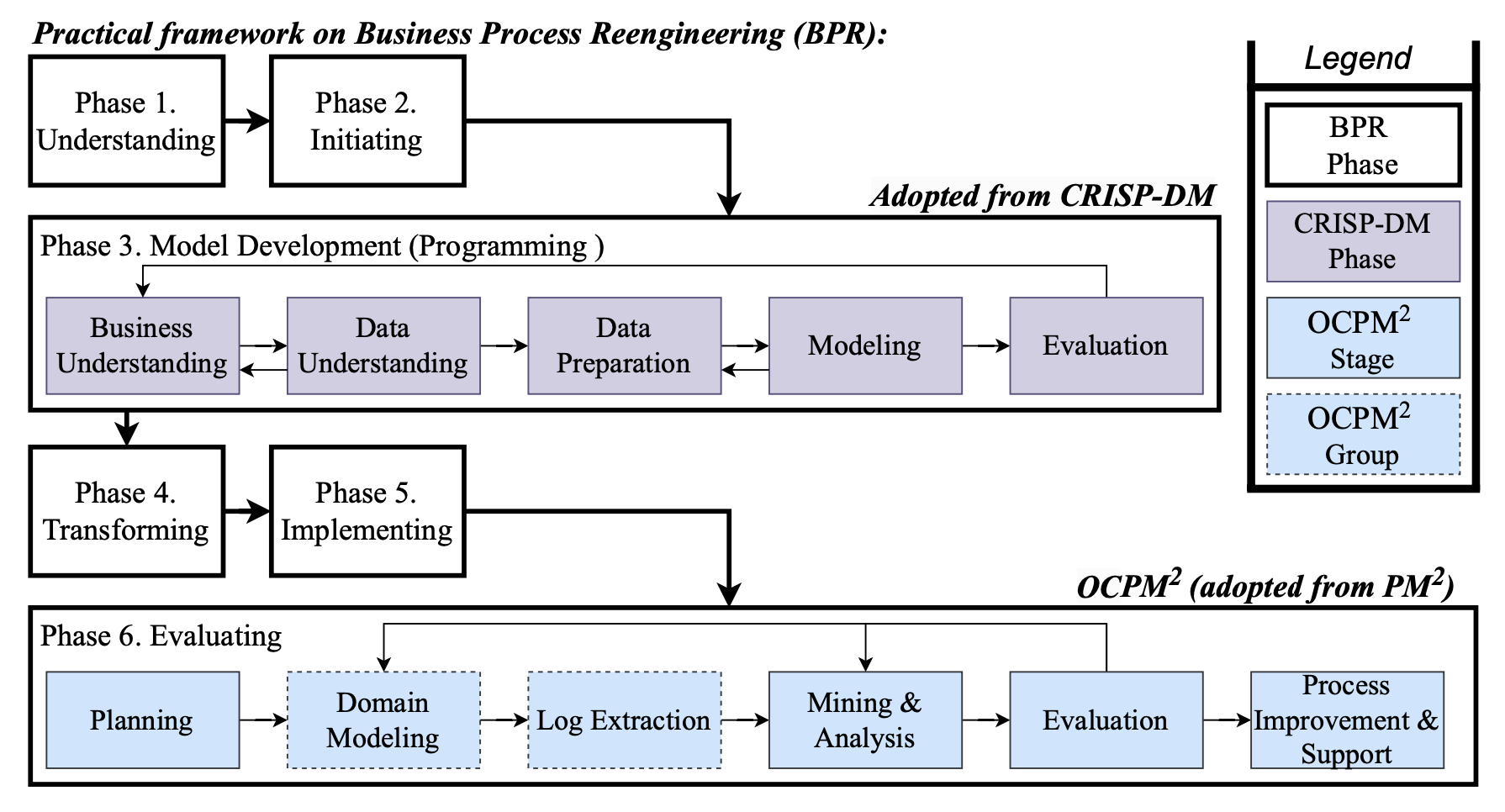
Fig. 1 illustrates the structured six-phase Business Process Reengineering (BPR) framework utilized in this study. Initial stakeholder engagement and extensive process documentation analysis provided a detailed foundation for validating the feasibility of AI-driven automation. This comprehensive approach enabled precise alignment of technical solutions with organizational and strategic goals.
Comparative Analysis and Best Practices
Comparing If Insurance’s experience with similar AI-driven automation initiatives across industries reveals common best practices and critical considerations:
- Systemic Thinking: AI interventions should be integrated within broader system-level improvements rather than isolated enhancements.
- Adaptive Capacity Planning: Organizations must proactively adapt resource allocations to handle the increased workload resulting from successful AI implementations.
- Simplified Communication: Detailed OCPM analytics require simplified visualizations (e.g., Directly-Follows Graphs) to effectively communicate complex interactions and outcomes to stakeholders.
Alternative approaches, such as incremental or phased automation and rigorous stakeholder training, also emerged as potentially viable strategies from comparative industry analyses. The explicit linkage of automation projects with overarching organizational goals ensures sustained alignment and supports broader digital transformation objectives.
Conclusion: Realizing Full Automation Potential
Effective AI-driven automation in complex business processes requires nuanced planning, rigorous methodological frameworks, and comprehensive analytical tools like OCPM. As demonstrated by If Insurance’s experience, successful automation initiatives depend critically on systemic understanding and proactive resource management.
Organizations seeking similar efficiencies should adopt integrated process evaluation methods, align automation strategies with broader operational goals, and prepare proactively for shifting resource demands. This strategic foresight transforms traditional bottlenecks into valuable opportunities—or “bottlenectar”—driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Cognaptus Insights: Automate the Present, Incubate the Future
-
[Submitted on 24 Apr 2025] AI-Enhanced Business Process Automation: A Case Study in the Insurance Domain Using Object-Centric Process Mining, Shahrzad Khayatbashi, Viktor Sjölind, Anders Granåker, Amin Jalali. arXiv:2504.17295 [cs.AI]. ↩︎
